Methacrylic anhydride
CAS NO: 760-93-0
Content: ≥ 97%
Packing: 200KG/drum.
Methacrylic anhydride (MAAH), plays a pivotal role in the polymer industry. Its reactivity and ability to modify polymers make it a valuable asset in various applications.This compound is known for its reactivity and is commonly used in the production of polymers, coatings, and adhesives.
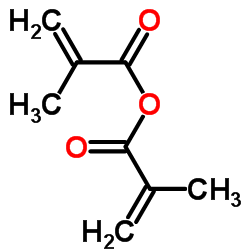
Molecular structure:
Molecular Formula: C8H10O3
Molecular weight: 154.1632
CAS NO: 760-93-0
EINECS NO: 212-084-8
Properties: colorless transparent liquid, stable at room temperature and pressure, density 1.035g/cm3, boiling point 87℃(13mmHg), refractive index 1.453, flash point 184℃.
Uses: Used in the synthesis of light-curing coatings, crosslinking resins and other materials, also used as raw materials for the synthesis of special fine chemicals.
Product quality standard: enterprise standard
| Indicator Name | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Content % ≥ | ≥ 96% |
| Methacrylic acid % ≤ | 2 |
| Standard stability | 2000ppm ± 200ppm |
Storage method: room temperature, avoiding light, ventilated and dry place.
Packing: Plastic lined iron drum, net weight 50KG/drum, 200KG/drum.
Dangerous goods symbol: xh
Danger symbol: R20 R41 R37/38
Safety marking: S26 S39
Dangerous goods transportation code: UN2927
Methacrylic anhydride Preparation Methods:
The existing technology mainly involves using acetic anhydride to react with the corresponding acid to prepare the corresponding anhydride, where the corresponding acid can be acrylic acid or methacrylic acid, etc. These methods include continuous or batch reactions, conducted in reaction/distillation apparatuses or distillation columns. However, existing methods have some problems such as polymerization reactions and low yields.
In contrast, our company proposes a new method for preparing methacrylic anhydride using a different technique. This method is a batch reaction, where acetic anhydride reacts with methacrylic acid, and the acetic acid generated during the reaction is gradually removed and replaced by introducing acetic anhydride and/or methacrylic acid into the reaction medium. This maintains the acetic acid concentration at a lower level during the reaction, thereby reducing the risk of polymerization and increasing the yield. This method offers higher production efficiency compared to existing technologies.
CH3COOCH3+CH2=CHCOOH→CH3COOCH2CH=CH2+CH3COOH
Methacrylic anhydride Applications:
The primary use of methacrylic anhydride is in the synthesis of polymers. It can introduce functional groups into polymers or monomers, enhancing their properties for specific applications. In coatings, it improves the durability and resistance to environmental factors. In adhesives, it contributes to the bond strength and longevity of the product.
1.Hydrogels and Cryogels:
One of the remarkable applications of MAAH is in the creation of hydrogels and cryogels. By functionalizing carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) with MA, researchers can produce photo-crosslinkable methacrylated carboxymethylcellulose (mCMC). This process allows for the design of hydrogels and cryogels with controlled structure and properties. These materials have significant potential in biomedical fields, such as tissue engineering, wound healing, and drug delivery, due to their biocompatibility and ability to mimic the extracellular matrix.
2.Coatings and Adhesives:
MAAH is also extensively used in the synthesis of coatings and adhesives. The introduction of MAAH into these products enhances their performance by improving durability, resistance to environmental factors, and bond strength. This makes MA an essential component in the manufacturing of industrial and consumer goods that require robust and long-lasting materials.
3.Biomedical Materials:
The biomedical industry benefits greatly from the use of MAAH. Polymers derived from MAAH can be tailored for specific applications, such as bone reconstruction, tissue scaffolds, and controlled drug release systems. The ability to fine-tune the properties of these polymers means that they can be designed to meet the stringent requirements of medical devices and implants.
4.Environmental Applications:
MAAH-based polymers are also finding their way into environmental applications. For instance, they can be used as thickening additives, pour point depressants, and viscosity index improvers for petroleum oils. These applications demonstrate the compound's utility in improving the performance and efficiency of petroleum products.
5.Inks and Coatings:
Another interesting application of MAAH is in the formulation of inks and coatings. As a casting polymer, MAAH contributes to the quality and functionality of inks used in printing and coatings applied to protect surfaces. Its properties help in achieving the desired consistency, adhesion, and finish for these products.
