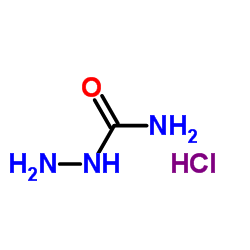
Semicarbazide Hydrochloride
semicarbazide hydrochloride. Its chemical formula is CH₅N₃O·HCl and its molecular weight is 111.53 g/mol. Semicarbazide hydrochloride is a derivative of urea, which is an organic compound that contains two amine groups and a carbonyl group. Semicarbazide hydrochloride belongs to the class of carboxylic acid hydrazides, which are compounds that have a carboxylic acid group (COOH) replaced by a hydrazine group (NHNH₂).
Physical Properties
Some of the physical properties of semicarbazide hydrochloride are:
- Color: white to light cream
- Shape: crystalline powder
- Odor: odorless
- Density: 1.286 g/cm³
- Melting point: 176 °C (decomposes)
- Boiling point: 235.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash point: 66.5 °C
- Solubility: soluble in water (>100 g/L at 15 °C), insoluble in absolute alcohol and ether
- Refractive index: 1.544 (estimated)
- Electrical conductivity: not available
Chemical Properties
Some of the chemical properties of semicarbazide hydrochloride are:
- Stability: stable under normal conditions, decomposes when heated above melting point
- Reactivity: reacts with strong oxidizing agents and bases
- Acidity: weakly acidic, pKa = 5.0
- Redox potential: not available
Preparation Methods
Semicarbazide hydrochloride can be prepared by various methods, such as:
- Reacting carbon monoxide with hydrazine at high pressure and temperature in the presence of a metal carbonyl catalyst
- Reacting nitrourea with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst, hydrochloric acid and an inert solvent
- Reacting urea with hydrazine hydrate at reflux temperature and then adding anhydrous hydrogen chloride
- Reacting hydrazine sulfate with potassium cyanate and then adding hydrochloric acid
One example of a preparation method is given below:
Urea (60.1 g, 1 mole) and 64% aqueous hydrazine solution (55 g, 1.10 moles) were placed in a 250 ml, 3-neck flask and heated at reflux (115°-120° C.) for three hours evolving gaseous ammonia. After the reaction was finished, the mixture was cooled to 70 °C, and 1.8 mol of hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise with stirring. The mixture was stirred for another 40 minutes, then cooled to 15 °C and filtered. The precipitate was dissolved again in absolute ethyl alcohol, filtered, and dried under vacuum at 120 °C to obtain the target product.
Uses and Effects
Semicarbazide hydrochloride has various uses and effects in different fields, such as:
- Pharmaceutical: it is used as a raw material for synthesizing nitrofuran antibacterials (such as furazolidone, nitrofurazone, nitrofurantoin) and related compounds, which have antiviral, antiinfective and antineoplastic activities
- Chemical analysis: it is used as a reagent for detecting carbonyl compounds as their semicarbazones, which produce crystalline compounds with characteristic melting points. It is also used as a solvent for chromatographic analysis and hormone separation
- Heterocyclic synthesis: it is used as a building block for synthesizing various heterocyclic compounds, such as pyrazoles, pyrazolines, pyrazolidines, triazoles, etc.
- Other: it is used as a urease substrate and a monoamine oxidase inhibitor10. It is also used as a pesticide and a photosensitive material
Safety Precautions
Semicarbazide hydrochloride is a hazardous substance that should be handled with care. Some of the safety precautions are:
- Wear appropriate protective gloves, clothing, and eye/face protection
- Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product
- Avoid breathing dust or fumes
- Wash hands and skin thoroughly after handling
- Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated place
- Dispose of the waste according to local regulations
- Seek medical attention if exposed or in case of any adverse effects
